BIREME/PAHO/WHO, in its mission to provide access to scientific and technical health information, aims to support the prevention and early diagnosis of diseases. In the context of health information, more specifically, in aspects related to the various types of cancer, the Virtual Health Library on Cancer Prevention and Control (or simply Cancer VHL) seeks to strengthen the integration between public and private institutions, in order to enhance the strengthening of the health information network.
This important source of information for researchers, health professionals, and society, launched in 2012, is the result of a technical cooperation project between the Pan American Health Organization Office in Brazil (PAHO Brazil) through the Latin American and Caribbean Center on Health Sciences Information (BIREME) and the José Alencar Gomes da Silva National Cancer Institute (INCA).
The Cancer VHL represents a model of technical cooperation committed to promoting the production and decentralized operation of knowledge in the area of cancer prevention and control. It seeks to disseminate relevant information and strengthen the creation of networks for information management in the area of cancer prevention and control.
In the last few months, there has been a realignment and management change in the Cancer VHL. Currently, it is in line with INCA’s strategic planning regarding the availability of reliable scientific and technical information for society. In addition, the Cancer VHL was incorporated into the INCA Library System Center and the institution’s Repository.
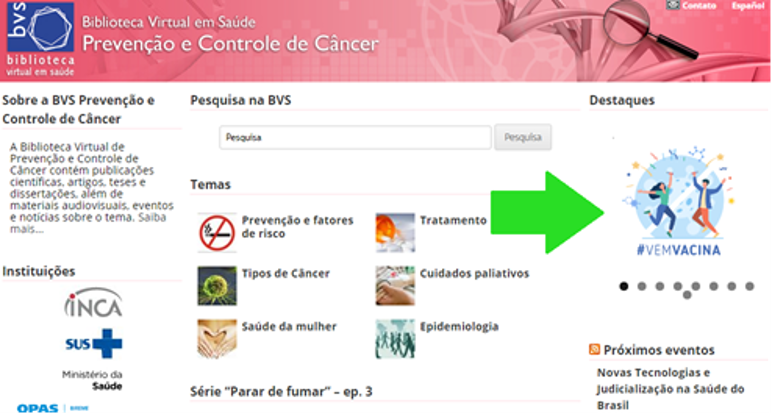 As a result of COVID-19, the actions of the Cancer VHL in 2020 were realigned to new actions and services that would contribute to the control of the pandemic. In the ‘Highlights’ menu, to the right of the homepage, podcasts, videos, and scientific publications from partner institutions (the Cochrane Library, AC Camargo Hospital, INCA, and the Tobacco Control Alliance, among others) were made available. In the central highlight of the VHL, in ‘Communication’, the following information sources were made available:
As a result of COVID-19, the actions of the Cancer VHL in 2020 were realigned to new actions and services that would contribute to the control of the pandemic. In the ‘Highlights’ menu, to the right of the homepage, podcasts, videos, and scientific publications from partner institutions (the Cochrane Library, AC Camargo Hospital, INCA, and the Tobacco Control Alliance, among others) were made available. In the central highlight of the VHL, in ‘Communication’, the following information sources were made available:
Special search strategies to assist the VHL user in the bibliographic survey of topics related to cancer prevention and control and topics that are part of the Ministry of Health’s campaign calendar. In addition to the topics mentioned, in 2020, strategies on cancer and COVID-19, and COVID-19 and vaccines were incorporated. In the News Carousel, instructional videos are disseminated that promote learning dynamically, with specific information.
In PUBCOVID19, real-time information is available, where you can quickly search for scientific articles on COVID-19 related to various health topics.
The Window of Knowledge is a resource with dynamic information, whose purpose is to present the content in a brief, yet effective and assertive way. The first topic chosen was National No Smoking Day: Smoking and Coronavirus.
 More recently, to mark World Cancer Day, the series of videos “Stop smoking” was created, also available on the INCA YouTube channel.[1]
More recently, to mark World Cancer Day, the series of videos “Stop smoking” was created, also available on the INCA YouTube channel.[1]
This set of new information sources in the Cancer Prevention and Control VHL aims to provide health professionals and researchers with specialized scientific literature, and at the same time, alert the public about ways to protect themselves from many types of cancer through the adoption of healthy lifestyle habits.
About World Cancer Day
Cancer is the second leading cause of death in the Americas, responsible for 4 million new cases and 1.4 million deaths in 2020 alone. Approximately 57% of new cancer cases and 47% of fatalities occurred in people younger than 69 years old. The most common types among men are prostate cancer (21.7%), lung cancer (8.9%), colorectal cancer (7.8%), bladder cancer (4.5%) and melanoma (3.4%). Among women, those with the highest incidence are breast (25.4%), lung (8.5%), colorectal (7.9%), thyroid (5%) and cervicouterine (3.8%) cancer.
The slogan for the World Cancer Day 2021 campaign is “I am and I will”, which was also the theme for 2020. PAHO/WHO joins the campaign and calls on everyone, collectively and individually, to join efforts in favor of actions that aim to reduce the impact of cancer on the population.
Many forms of cancer can be prevented and controlled through evidence-based strategies for prevention, early detection, screening, and treatment.
 The risk factors that can be altered by changes in the most common lifestyles for cancer, which are common to many other non-communicable diseases, are: consumption of tobacco products, diet poor in fruits and vegetables, alcohol abuse, and lack of physical activity. There are also specific risk factors for cancer, which include chronic infection of the human papilloma virus (HPV) for cervical cancer; hepatitis B and C for liver cancer; and H. pylori for stomach cancer. Between 30 and 50% of cancer cases could be prevented by reducing the prevalence of known risk factors. Proven examples of interventions that produce striking results are tobacco control (which prevents lung cancer) and HPV vaccination (which prevents cervical cancer). Public health and health promotion messages prepared by national health authorities should provide evidence on specific risk factors and ways to protect oneself.
The risk factors that can be altered by changes in the most common lifestyles for cancer, which are common to many other non-communicable diseases, are: consumption of tobacco products, diet poor in fruits and vegetables, alcohol abuse, and lack of physical activity. There are also specific risk factors for cancer, which include chronic infection of the human papilloma virus (HPV) for cervical cancer; hepatitis B and C for liver cancer; and H. pylori for stomach cancer. Between 30 and 50% of cancer cases could be prevented by reducing the prevalence of known risk factors. Proven examples of interventions that produce striking results are tobacco control (which prevents lung cancer) and HPV vaccination (which prevents cervical cancer). Public health and health promotion messages prepared by national health authorities should provide evidence on specific risk factors and ways to protect oneself.
PAHO/WHO works permanently with its Member Countries on several aspects related to cancer prevention and control. Advanced stage diagnosis is common, especially where health systems are not robust. The effective early diagnosis of cancer can be achieved by raising awareness among the public and health professionals about the signs and symptoms of cancer, establishing referral systems, offering rapid clinical and pathological diagnosis, and appropriate treatment and supportive care.
Various types of cancer, mainly cervical, breast, and colorectal, can be detected in early stages in asymptomatic people, with affordable screening tests, which, in conjunction with diagnosis and treatment, can save lives.
Cancer control planning begins with the collection and analysis of data on trends in incidence and mortality, prevalence of risk factors, and current capacity and system performance. In this sense, cancer registries are an important part of disease control.
Links of interest
National Cancer Institute – NIH
Instituto Nacional do Câncer (in Portuguese)
Fundação do Câncer (in Portuguese)
World Health Organization. World Cancer Report: Cancer Research for Cancer Prevention. 2020. Edited by Wild CP, Weiderpass E, Stewart BW. Available at: http://publications.iarc.fr/586
[1] BIREME acknowledges the contribution in this news by Robson Martins, Head of the Integrated Library System Nucleus, Education Department of the National Cancer Institute, Ministry of Health of Brazil.